Skin Sturcture&Skin types Classification
Hi everyone, my name is Anton Sabenin, I think most of you already know me as administrator of Anna Dixon and Maryann Hoang courses, but I’m not only the administrator, I create this website for all of you to save all the information and not to lose it also I’m working with laser tattoo removing over 4 years every day and want to share my experience with you. In most countries you need a medical license for tattoo removal procedure, but where I am living I don’t need it, and mostly every artist working with laser removal, some of them do it right, and some of them do it really wrong… So I want to teach you to understand this procedure, how the laser works on the skin, what can be removed and what cannot, how to not harm your clients and not to do keloids on their skin.
I’m so glad that you decide to take my course. You can ask me any questions right after the lesson, or in the forum for this course. The forum will open automatically when you bought this course.
So let’s start.
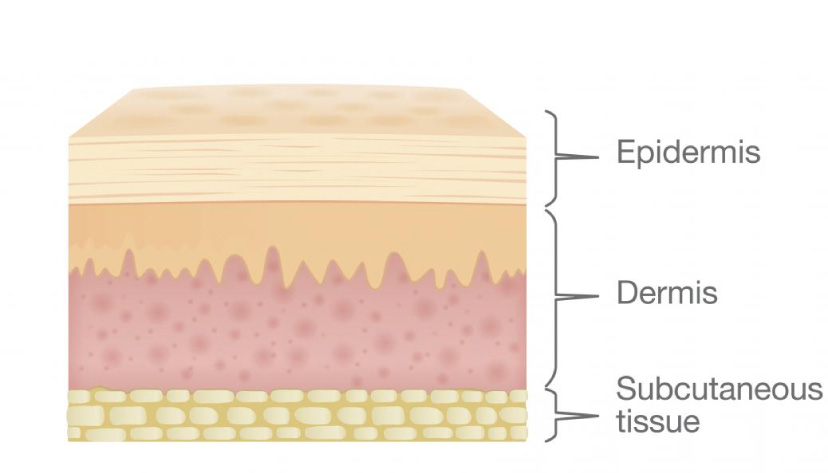
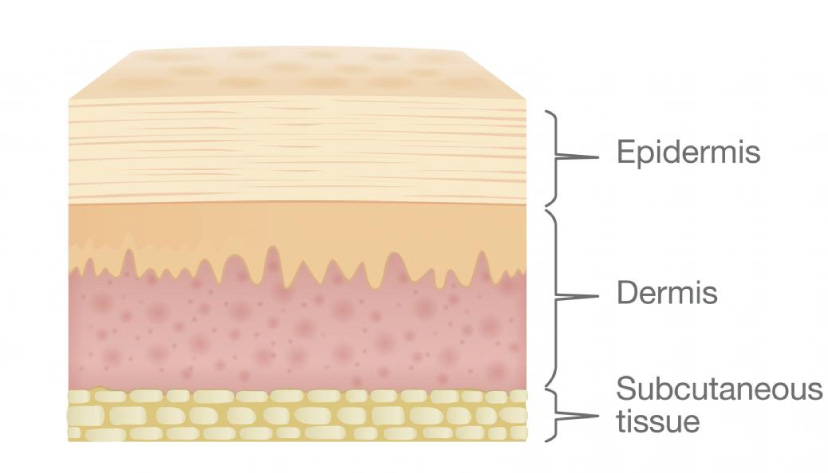
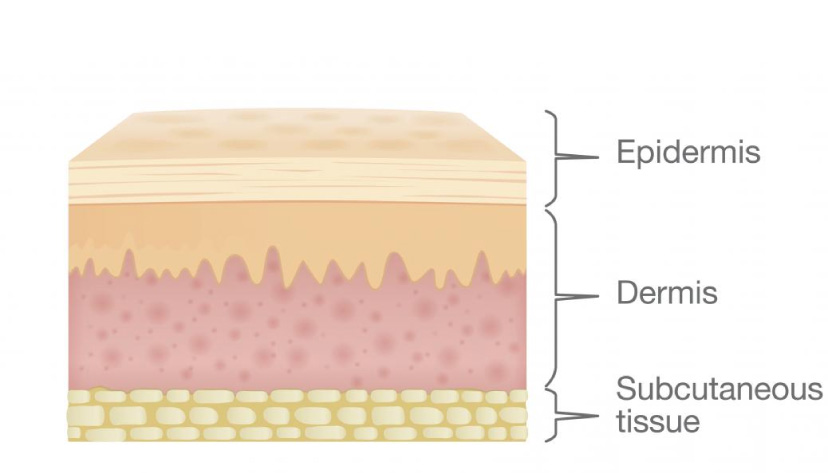
First of all, I want to remind you of skin layers because it’s very important to know it, and this will be needed on the next lessons to understand all material and how the laser works on the skin.
Let’s talk about Epidermis structure because in permanent makeup we working only in epidermis.
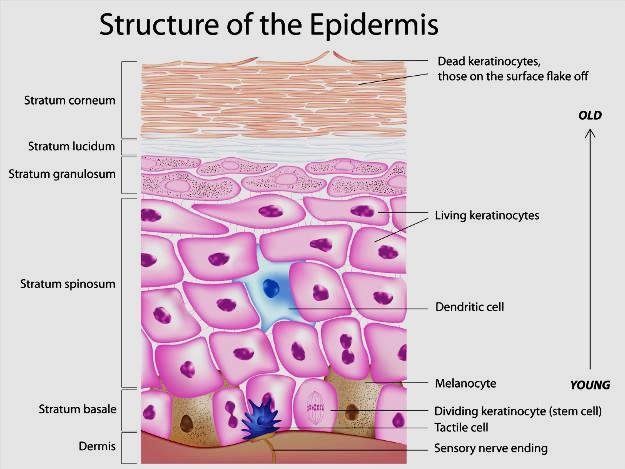
The First Layer is
BASAL LAYER
The basal layer is the lowest and roughly speaking lies on the border with the dermis and it has just one layer of cells. These cells have only one task – they dividing at the same time only 40% of cells are dividing ) All the rest come into work in some critical situations, for example of skin trauma.
At the same time, the cells are constantly dividing and their quantity is constantly growing. This leads to the fact that new cells are constantly going to the upper layers.
That means that the epidermis is constantly updating with new cells and the old ones are constantly peeling off from the upper layer and this process proceeds all-time in our life.
Cells from the Basal layer are going into Spinous layer
SPINOUS LAYER
Cells in this layer are more squared, and as close to the Granular layer they become flatter.
Why this layer calls Spinous? That because of the layer formed by keratinocytes. The layer contains ten or more rows. Langerhans cells are located in the lower rows. Keratinocytes have characteristic processes – “spikes”(desmosoms) with which they are connected with each other. In addition to general-purpose organelles, there are keratinosomes (granules of Odland) – modified lysosomes surrounded by a membrane and a modified tonofibrillary apparatus, forming concentric thickening around the nucleus. His function is the mechanical protection of the cell nucleus from damage.
Ok, the next layer is
GRANULAR LAYER
This is the layer of aged cells, It has 1-2 rows of cells stretched parallel to the skin. Quantity of organelles decreases, the cytoplasm contains keratohyalin granules associated with tonofibrils. There are also had keratonosomes. The contents of these granules are released in the upper rows of the granular layer, where lamellar structures are forming from it. Such structures are hydrophobic and prevent the penetration of water into the underlying layers. Also here begins the synthesis of keratolinin and filaggrin, due to which keratohyalin is formed and further keratinization of the epithelium.
CLEAR LAYER
This layer looks like a shiny homogeneous strip of pinkish color. It consists of 1-2 rows of flat cells with unexpressed boundaries, devoid of nuclei and organelles. It is well developed on the palms and soles.
CORNIFIED LAYER
This is our shield ) The stratum corneum performs a protective function from chemical and mechanical damage and has no living cells. The layer is formed by horny scales – dead keratinocytes connected by interdigitations of their cytolemmas. The thickness of this layer directly depends on the intensity of the mechanical load on the skin area.
It all the same cell with their life, from young on the lowes layer to old on the highest.
And what is interesting, this process takes from 20 to 50 and more days. Average we take 30 days and we said it for our clients)
Why we said to our clients, that correction only after 30 days?
We waiting for regeneration process of skin to see which areas are not colored.
But need to understand, that we are all different and it can take more time than 30 days for skin regeneration especially for old ladies because the regeneration process of old peoples going slower.
For this type of client recommendations to make corrections a little bit later, for example, 40-50 days. It will give you a more detailed picture where you need to put pigment else.
- And one more from interesting things
Сritical role of the scar-forming playing basement membrane. The basement membrane is the border between the epidermis and the dermis
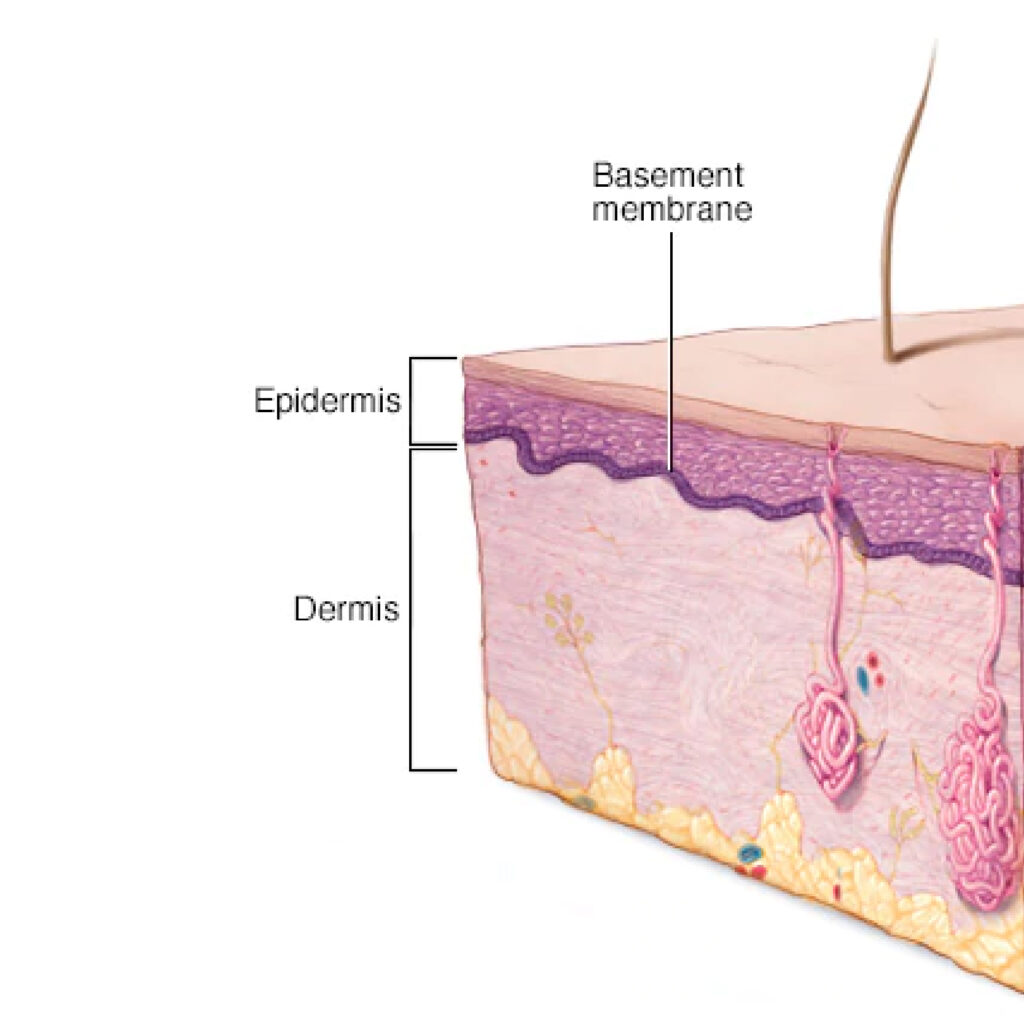
The basement membrane(BM) has a different structure of collagen fibers etc. Normal property of BM to regulate how quick the epidermis divides and mature, and how well the dermis function. When it occurs skin damage, for example, mechanical damages, burns, the basement membrane become broken. Interaction and regulation between the dermis and the epidermis are broken.
Ok, This is our skin under the microscope
This is CORNIFIED LAYER which protects lower layers from any mechanical or chemical or thermal damages )
Ok, lets’ continue
In the epidermis, we also have some more cells and let’s talk about
Some of us like taking sunbathes, and like when skin looks darker, but if to see on this from different angle tan is harmful. Tan is a reaction of our skin on ultraviolet damage. The pigment of our skin placed only in the epidermis and it determines our skin color.
Pigments in permanent make up are placed deeper then epidermis and the epidermis layer performs the function of the light filter, which changes color perception.
For example, If you take VI skin type you will never get the bright effect on their lips, no matter how hard you try, because the top layer of the skin saturated with melanin which gives brown color.
And another such moment, epidermal cells cannot produce pigment of our skin, they don’t have permission for that ))
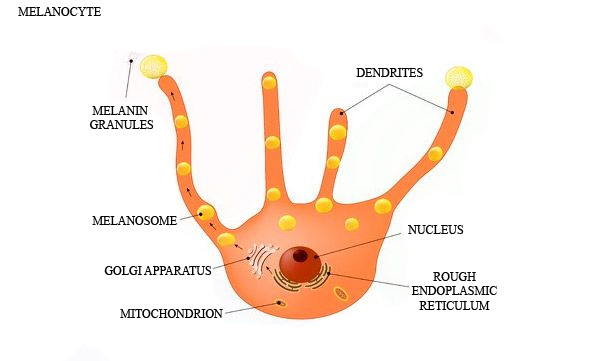
This function is performed by melanocyte.
Melanocytes are placed in the Basal Skin Layer.
Melanocytes have only one main role – synthesis of natural skin pigment – MELANIN.
We have two types of melanin:
Eumelanin – black and brown pigment
Pheomelanin – reddish and yellowish shades
From a combination of these two types of melanin determine our hair, eyes, skin, etc. colors.
Also for all people, the approximate quantity of melanocytes is equal, it’s 1 melanocyte for 50 basal layer cells. And when the cell in the epidermis in their life process going through DENDRITES they get some portion of melanin. This process determines your skin color.
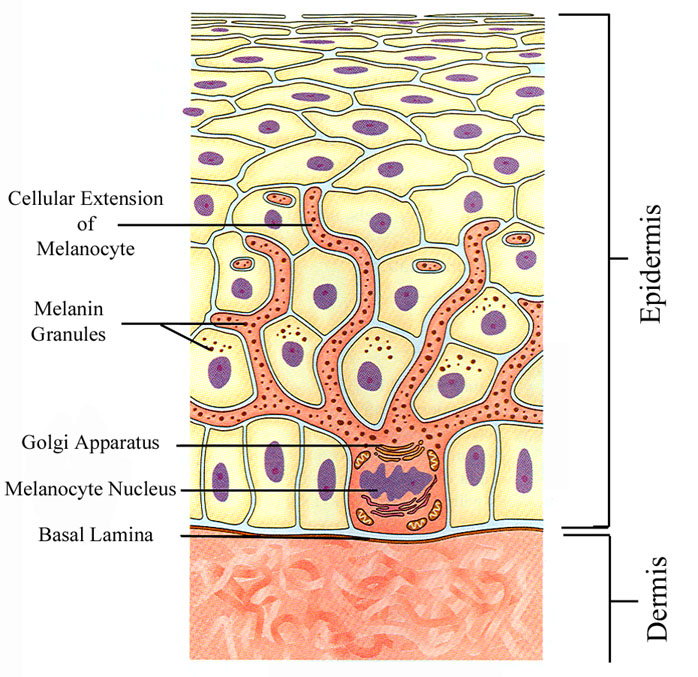
And when we take sunbaths, melanocytes going crazy and give to us more melanin. If you have dark skin, melanocytes adapting very fast, but if your skin is white you get a sunburn, because melanocytes can’t give enough melanin )
Here is the difference between Dark and Light Skin
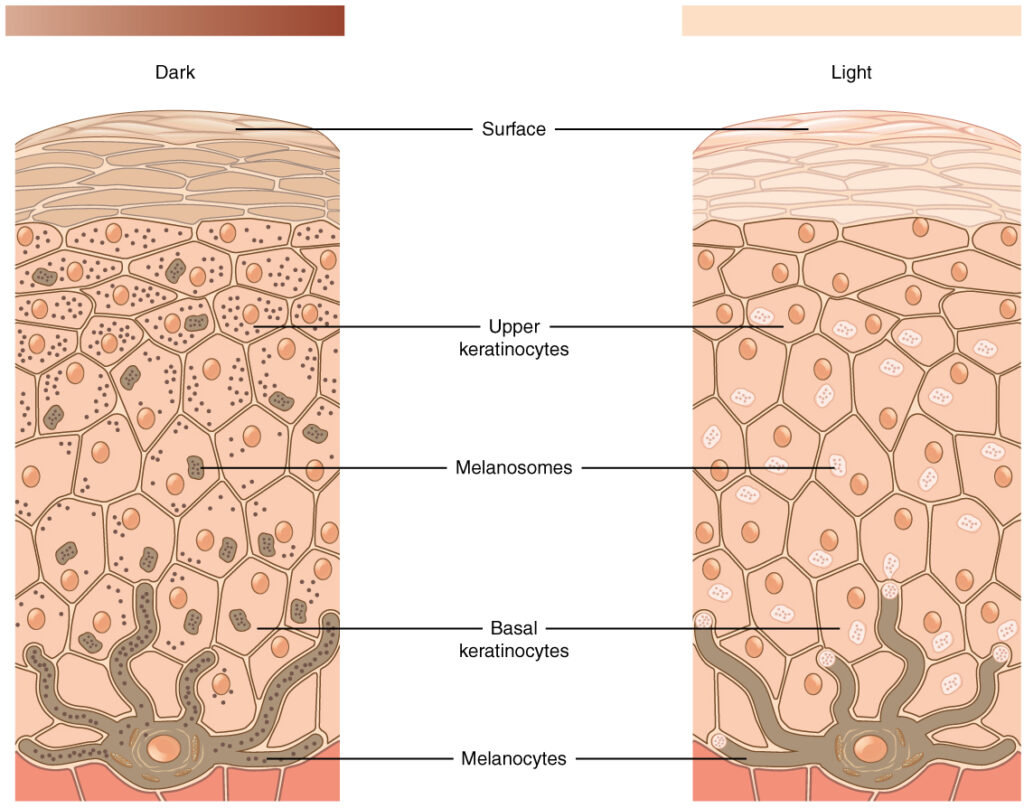
Light skin has not much Melanin Granules, and in the dark skin, melanocyte working very active and gives melanin in much bigger portions, as a result, we have colored by melanin skin.
For permanent makeup, it’s very important from the side of color perception.
And for Laser Removal it’s bad because epidermis lays on the way of laser light because laser should go through the epidermis to derma where tattoo pigments lay and melanin absorbs laser flash.
Classification of skin types was created in connection with this by Thomas Fitzpatrick
It calls Fitzpatrick scale
All Skin types are divided into 6 skin types

- 1 skin phototype (Scandinavian)
Includes people with light, thin skin and red or blond hair. They are characterized by the presence of freckles and light eye (blue, green) color.
Tolerance of ultraviolet radiation in people with the first phototype of the skin is minimal – after a few minutes of being in direct sunlight, an inflammatory reaction occurs (the skin burns). Uniform tan does not occur.

- 2 skin phototype (light-skinned European)
Includes people with fair skin and blond hair. Freckles can occur, but less than people with the first skin phototype.
Eye color is light blue, gray, green.
Under the influence of sunlight, the skin burns easily. To achieve a pronounced natural tan is difficult.
The use of photoprotective agents is mandatory.

- 3 skin phototype (Central European)
Includes people with ivory skin, light and dark brown hair.
The characteristic color of the eyes is light brown.
The skin burns easily, the tan is beautiful and uniform, but with prolonged exposure to direct sunlight can burn.
The use of sunscreen is necessary.

- 4 skin phototype (Mediterranean)
By the IV type are people with olive skin color, dark brown and black hair.
It is characterized by dark brown or black eyes.
The skin almost does not burn, tan arises quickly and lasts a long time ..
The use of sunscreen is necessary for prolonged exposure to sun exposure (not so much to prevent sunburn, but rather to prevent premature aging of the skin)

- 5 skin phototype (Asian)
Includes faces with brown, yellow or yellow-brown skin and black hair.
The skin of the fourth phototype never burns. Tan is hardly noticeable against the background of natural skin pigmentation.
The use of sunscreen is not necessary.

- 6 skin phototype (African)
Persons with dark (black) skin color, dark eyes, and black hair.
The skin of the sixth phototype never burns.
Natural protection of the skin against ultraviolet radiation is so strong that there is no need to use sunscreen.
In the laser removal process, you should be very accurate with 5-6 Type of skin, effective from laser removal procedure on this type of skin will be worse than on other types. And danger will be higher due to the high concentration of melanin in the skin, traumatization risk higher.
Why our skin has so hard protected structure?
What for we need melanin?
It formed many many years ago, first of all, this is the protection of Basal layer cells because cell dividing it’s a very complicated process. Every cell dividing
accompanied by a complete doubling of all genetic information about a person.
In theory, to say with simple words, can recover the whole person from one cell because cell has all genetic information.
And when cell dividing and they are dividing too much (45-50 Days for all epidermis refresh). If at this time will act some skin damage factor-like hard UV, it will come to the wrong cell dividing process, mutation, etc. In fact that if a person many times get burned by sun especially when was young, then in future more risk to get skin oncology, is the result of skin damage and mutation by UV. The same effect for skin can give radiation, but it’s not so common, like sun UV.
So in this way, our organism has learned to protect from sun UV by melanin.
But when UV effect on Basal layer of the epidermis it affects harder to the deeper dermal skin layers, and it causes photocarcinogenesis
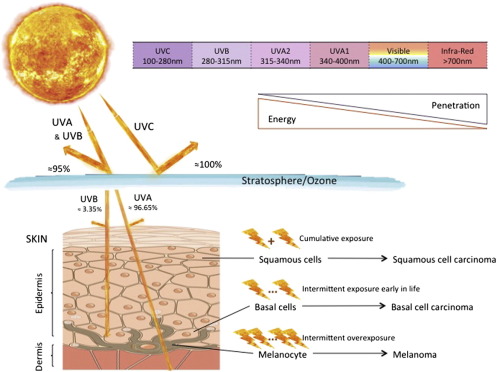
Here is most know example
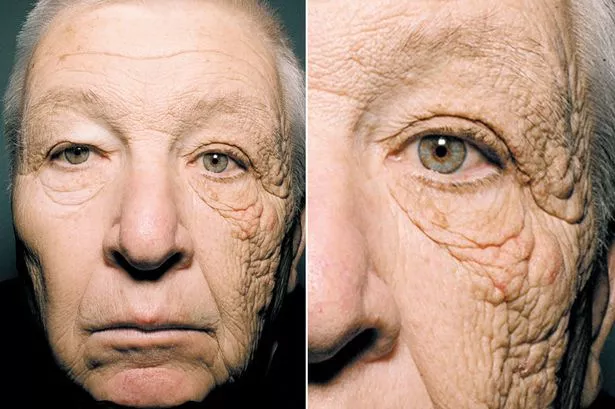
This is the portrait of the 69-year-old Left Handed Truck driver shows how the sun has damaged the left side of his face. He drives his truck for over 28 years, and this is the result of sun damage. And you see the signs of rapid aging of his left side of the face. Peoples from south regions are more prone to skin photoaging. So I want to warn you from sun rays, solarium, etc )
So that was about epidermis.
Now let’s go deeper to our skin, where we working with permanent make up
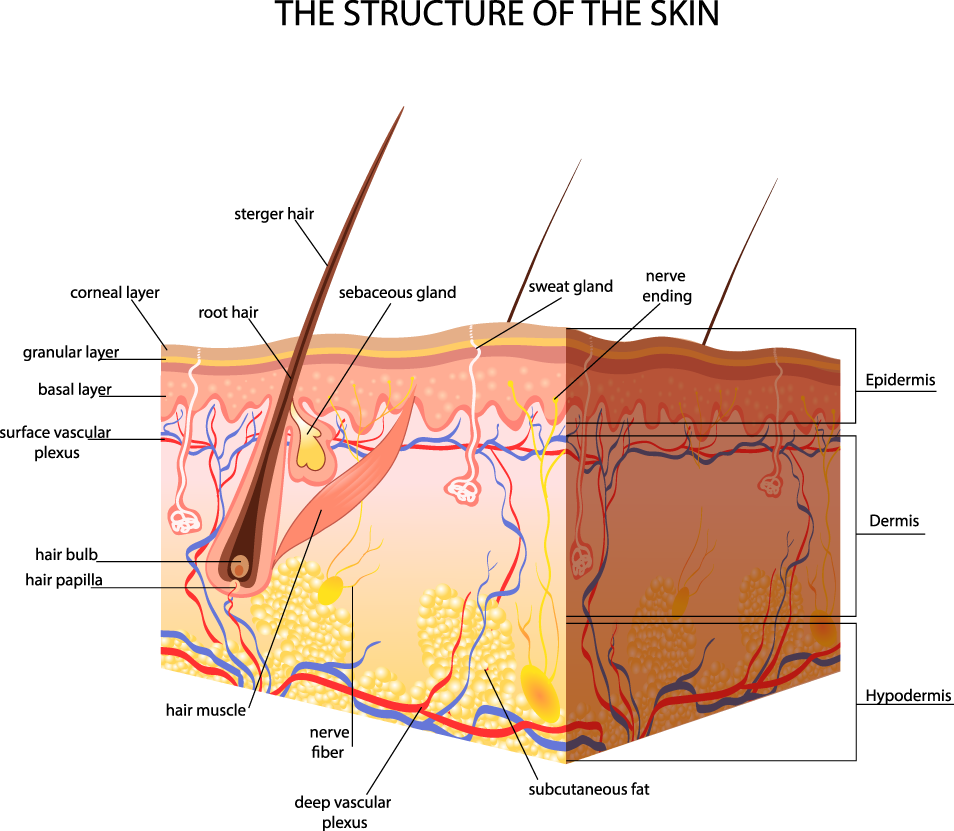
Dermis
How dermis and epidermis connected to each other?
It looks like hills
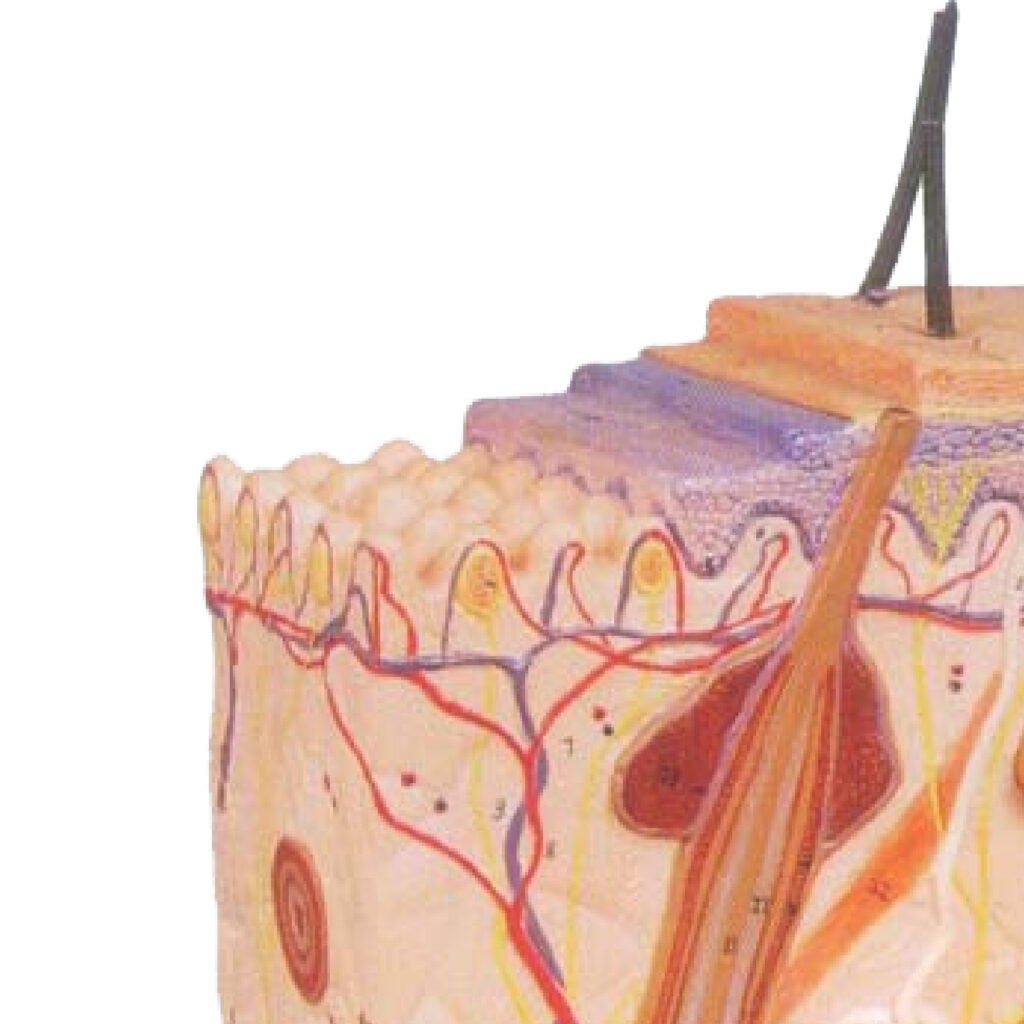
Why like this? Because
- In the epidermis, there are no vessels and capillaries. All nutrition of the epidermis occurs through the dermis. You can see it on photo upper, on each hill there are capillaries, and through this capillaries the epidermis fed. You remember, that the lowest layer of the epidermis is most active, and other cells from upper layers have lower activity.
- This structure allows keeping well the epidermis

Derma divided into layers
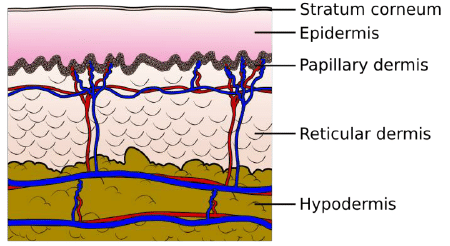
Papillary Dermis is less durable, the main function is the nutrition of the epidermis.
Reticular Dermis has more strong structure, the main function is mechanical strength, this is the base of our skin. The quantity of fibers in the reticular dermis is greater, they ruder and dominated by collagen fibers.
So where are we putting our pigments?
First of all, we should understand, that the pigment should go through the epidermis, it should lay lower than the basal layer.
If at some conference you will hear from a speaker that we working superficially in the epidermis, you should know, that it’s not true. Yes, the pigment in proceeding goes to the epidermis, but in 1-2 months the epidermis will be refreshed and pigment will fade out.
For good retention, the pigment should be put in Papillary Dermis – it’s in an ideal. It should be put maximal upper in the dermis, not too deep. If the pigment will be higher, then you will have a more predictable result.
Ok, let’s continue.
What the dermis contain?
- Fibroblast
(Fibroblasts synthesize and secrete the main components of the intercellular substance: polysaccharides, collagen and elastin precursors, etc. Fibroblasts, at age, turn into fibrocytes, which very weakly synthesize the components of the intercellular substance RVST.)
- Fibers
Collagen – mechanical strong function
Elastine – possess extensibility
- Extracellular substance – this is the substance which fills all space between cells and fibers
Hyaluronic acid
Сhondroitin sulfates
Glycosaminoglycans
Why are we talking about dermis? Because of this the part with which we will work with you. All process mainly going in the dermis.
- Many artists mistakenly believe that the dermis is very static. This belief often leads to mistakes.
- If we put the pigment to the skin through injury, as it usually happens and if we use a laser, where will the pigment go from there?
At this moment, the biggest misconception arises – in order for the pigment to come out of the skin, we need to destroy the skin in the same way and only then the pigment will come out.
This is ABSOLUTELY WRONG!
By its nature, the dermis is very active, but we notice this only when we get damaged skin, for example, a cut, etc. After 7-14 days, you can see that the skin recovers, it regenerates.
Replacement, synthesis, breakdown of collagen fibers constantly occur in the dermis. We do not notice it at first glance, but if we take, for example, selfies taken 6-7 years ago, we will see the changes that are happening to us.
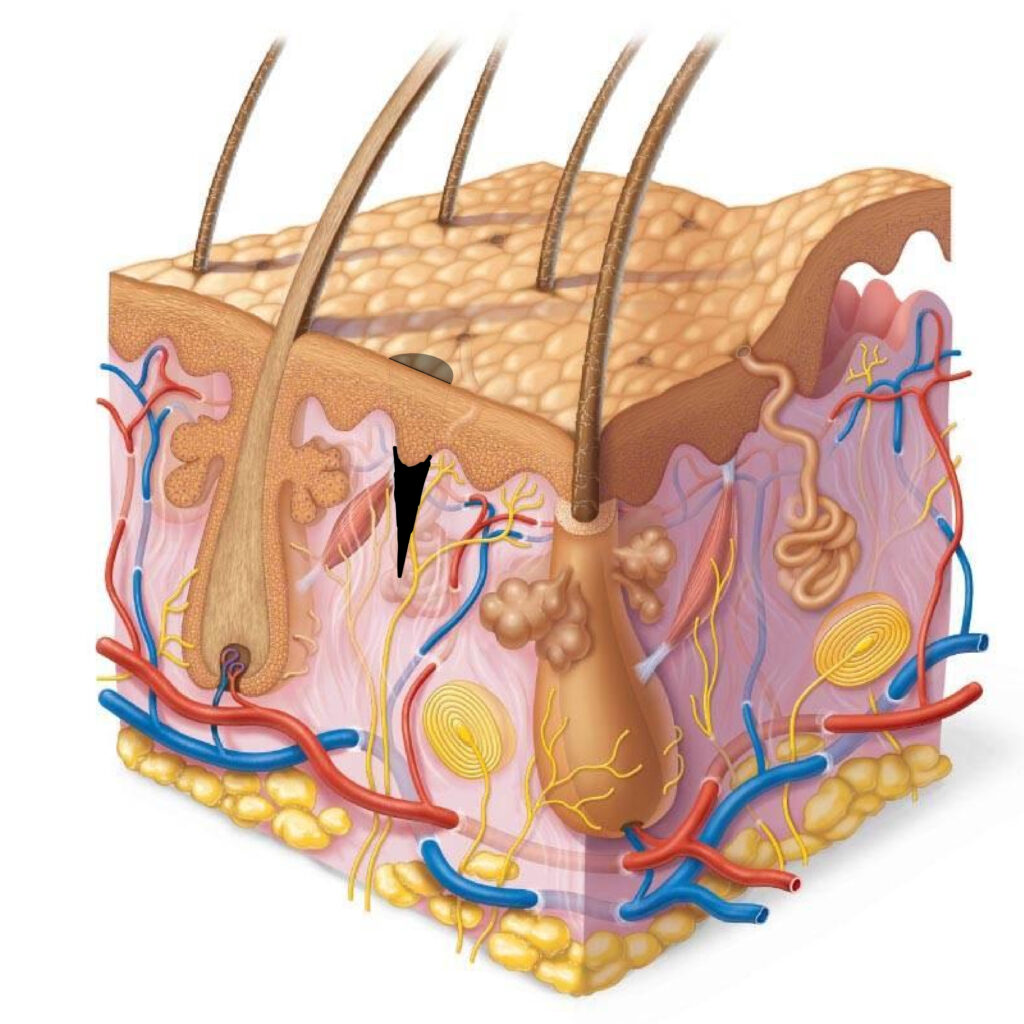
So when we put pigment into the skin, it gets involved in the whole process. In addition, the dermis has vessels, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, hair follicles, vascular plexus, nerve endings, etc.
In addition to fibroblasts that build our skin in the dermis, there are also immune cells – macrophages (they are present in all tissues of our body, not only in the dermis)
Their main task is to struggle with foreign substances. When macrophages meet such substances in the body, they start thinking about what to do with it. The first thing they will try to do is to “eat”.
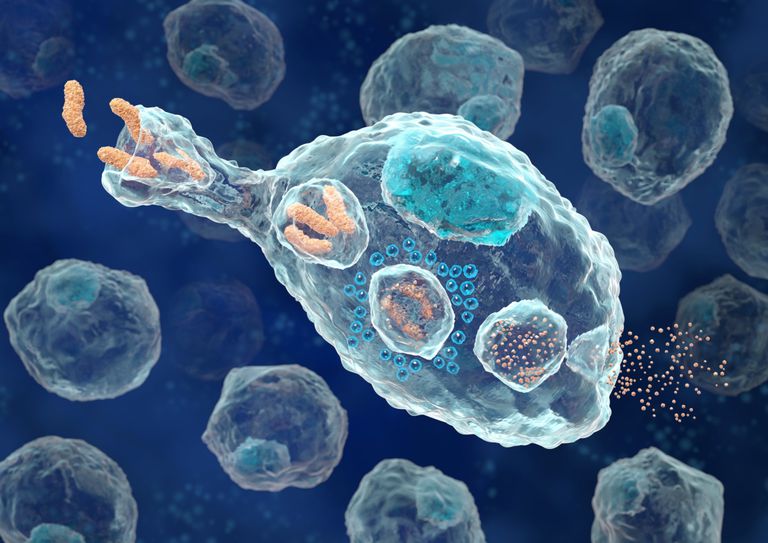
In this photo, a macrophage eats bacteria. It also comes with a pigment, which in fact should not be present in the skin. The macrophage breaks it down with its enzymes. If it can not break down, then it can bring it beyond the dermis to the nearest lymph node, where it will try to do something, or leave it there filtered. If a macrophage can neither move it nor digest a bacteria, then it tries to isolate the substance from the surrounding organism and remains in this state for a long time.
What happens when we put pigment into the skin?
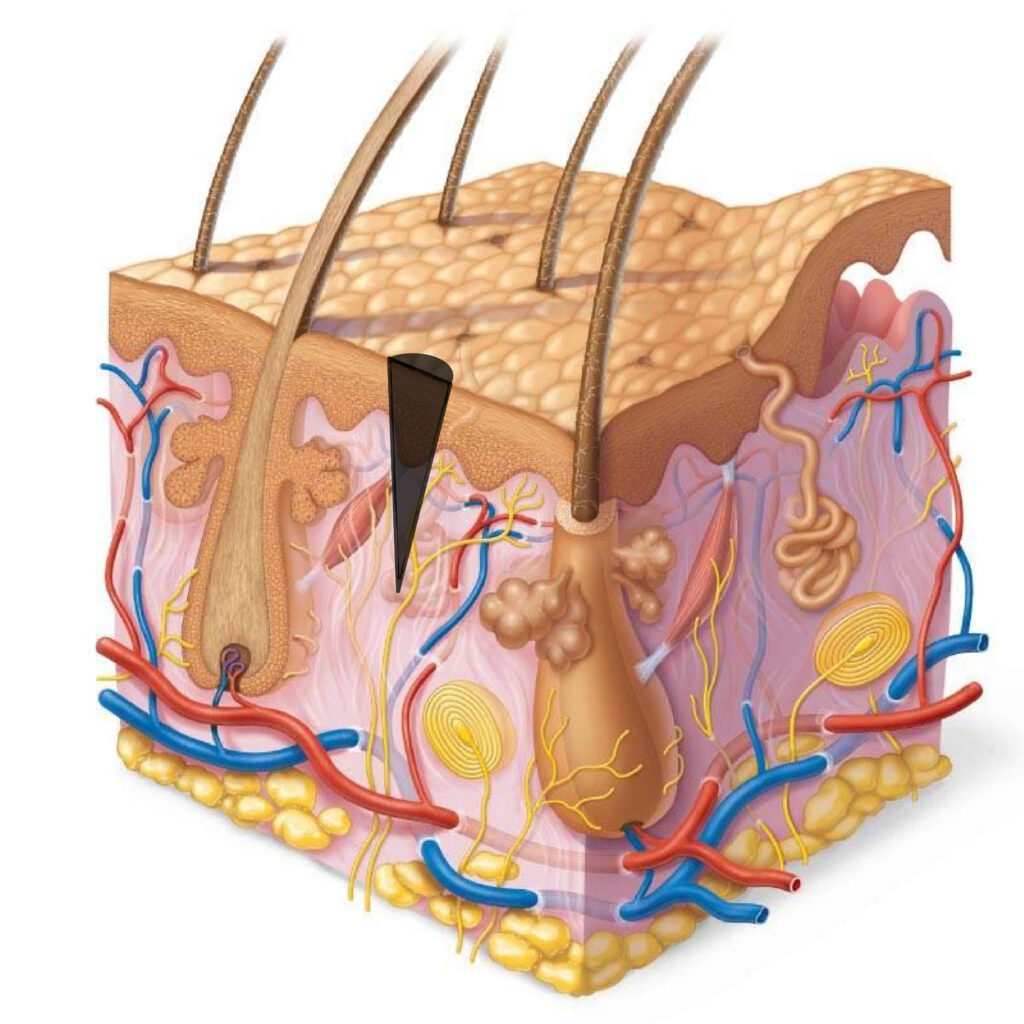
Staining of both the epidermis and the dermis occurs. That is why we have a strong effect immediately after the procedure, and in 30-40 days the brightness will decrease by 40-50%. We will see the real residue and correct our permanent makeup at the correction.
It looks like this:
After 15 days
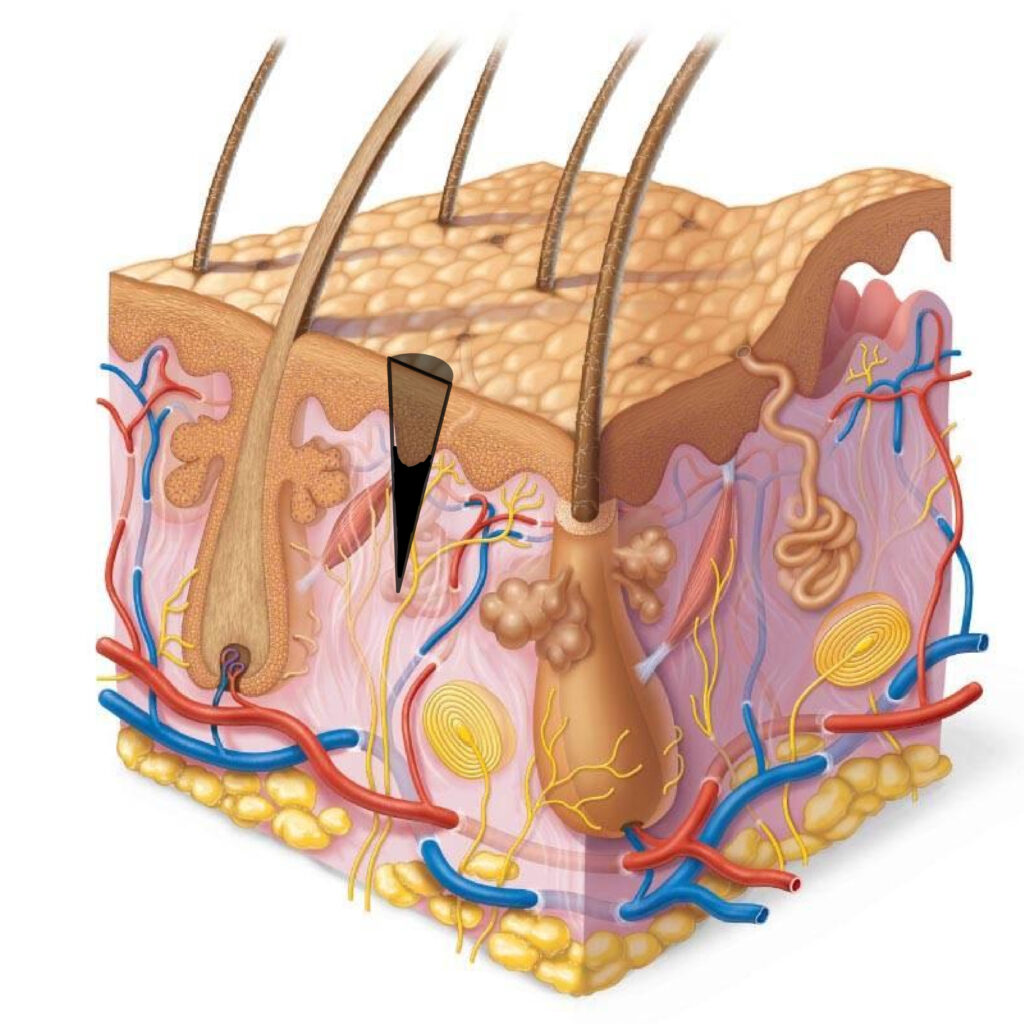
A month later, the epidermis is regenerated, and we see the real pigment residue in the dermis, on the basis of which we make corrections to our clients.
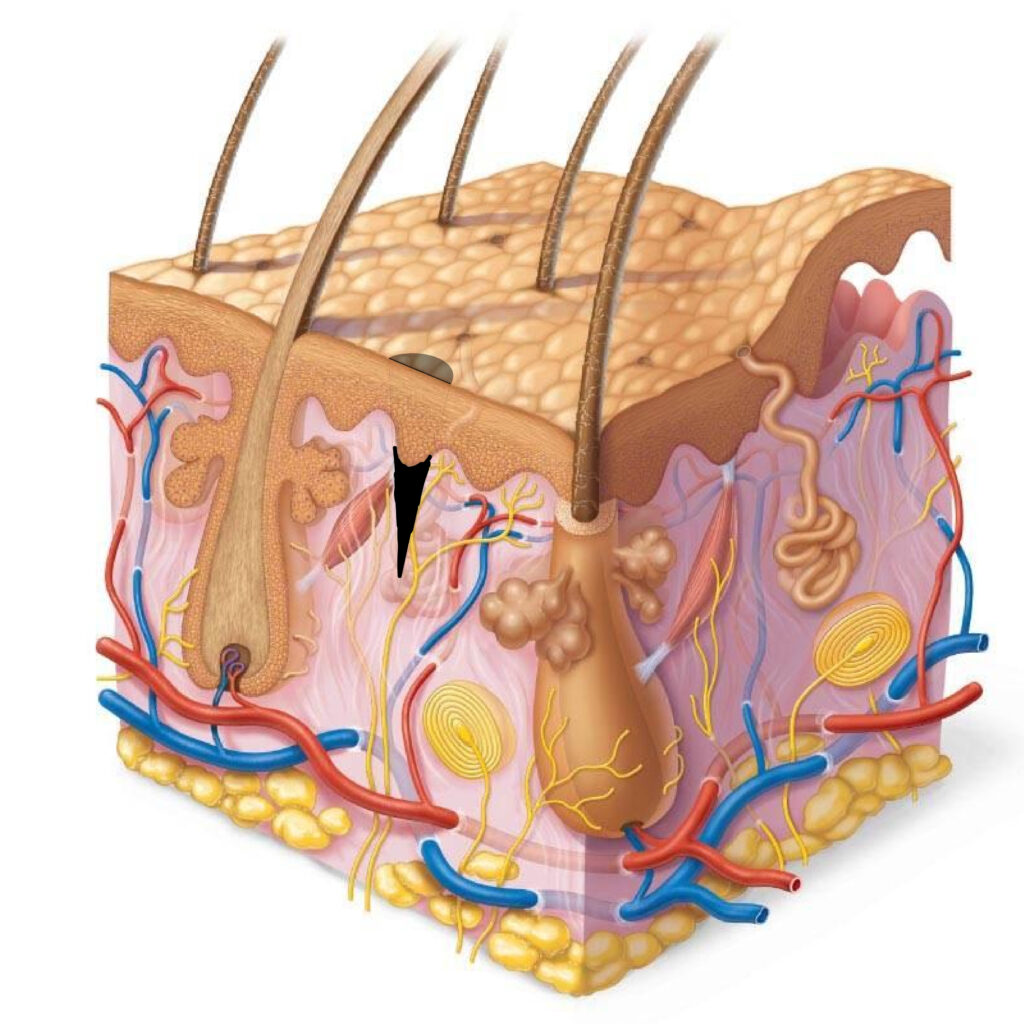
OK, what happens next, as this is not the end) You will probably agree that after the correction in two or three months, permanent makeup changes its color, brightness, etc. This is especially noticeable in the hair technique, any hardware technique or microblading. After six months or a year, the hair will still blur, no matter how cool you do it. At the same time, on oily skin, it will blur faster than 6-9 months, on normal skin 1-1.5 years, on dry skin it can last up to 2 years.
Why is this happening? We have already analyzed the fact that the dermis is a dynamic tissue, so, over time, something like this happens.
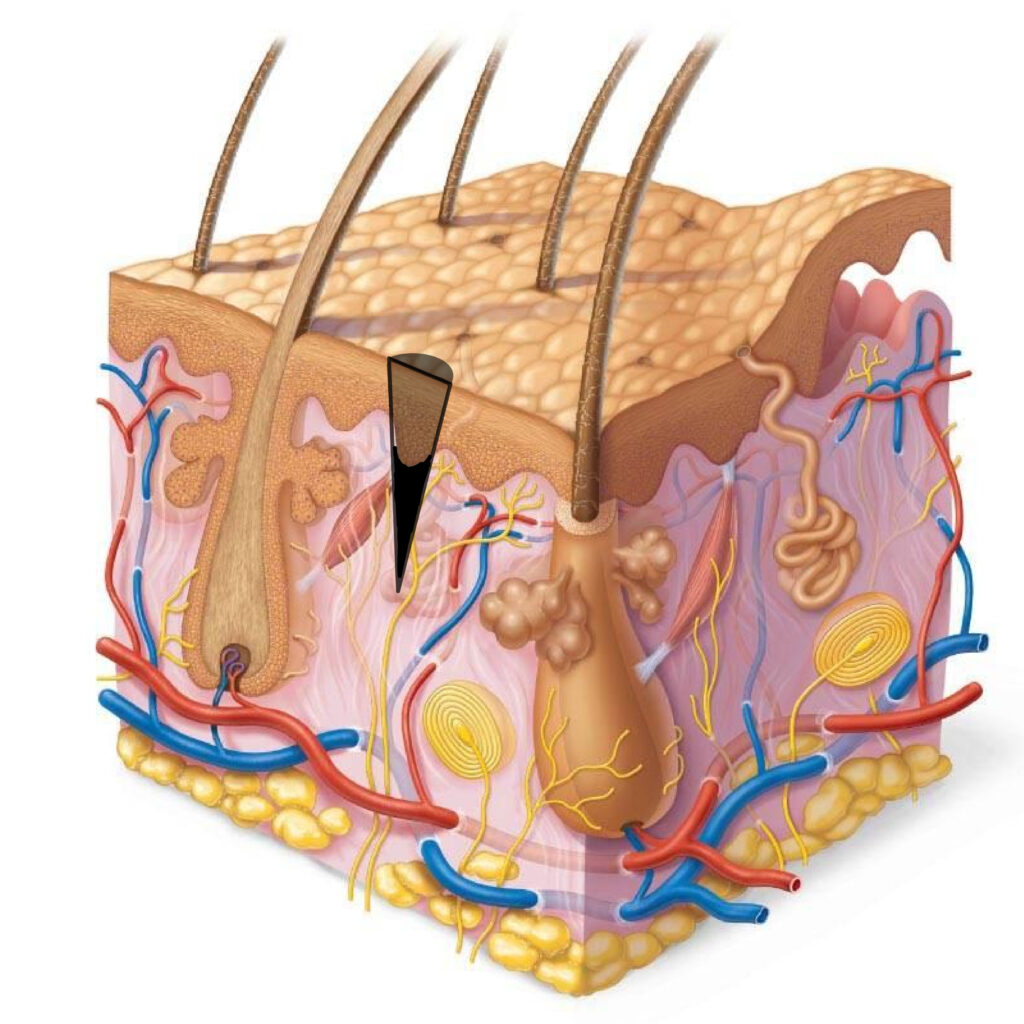
The pigment particles move in the dermis due to its restructuring. Therefore, do not blame yourself if the hairs blur through these intervals, since there is no one to blame, this is how our system works.
Another important point for understanding how the pigment lies in the skin.
The pigment lies unevenly in the skin. On one level you will not be able to put it in any way and such conversations as “we will now cover it with the new layer is not correct at all.” If someone has thoughts to cover the permanent makeup and put it higher, do not even try, it will not work, you just mix the old and new pigment in the skin.
With laser removal, the pigment is also unevenly broken, and what is more deeply will be removed worse. Laser removal is generally an unpredictable process since there may be a large unevenness during removal.
Now let’s talk about the thickness of the skin
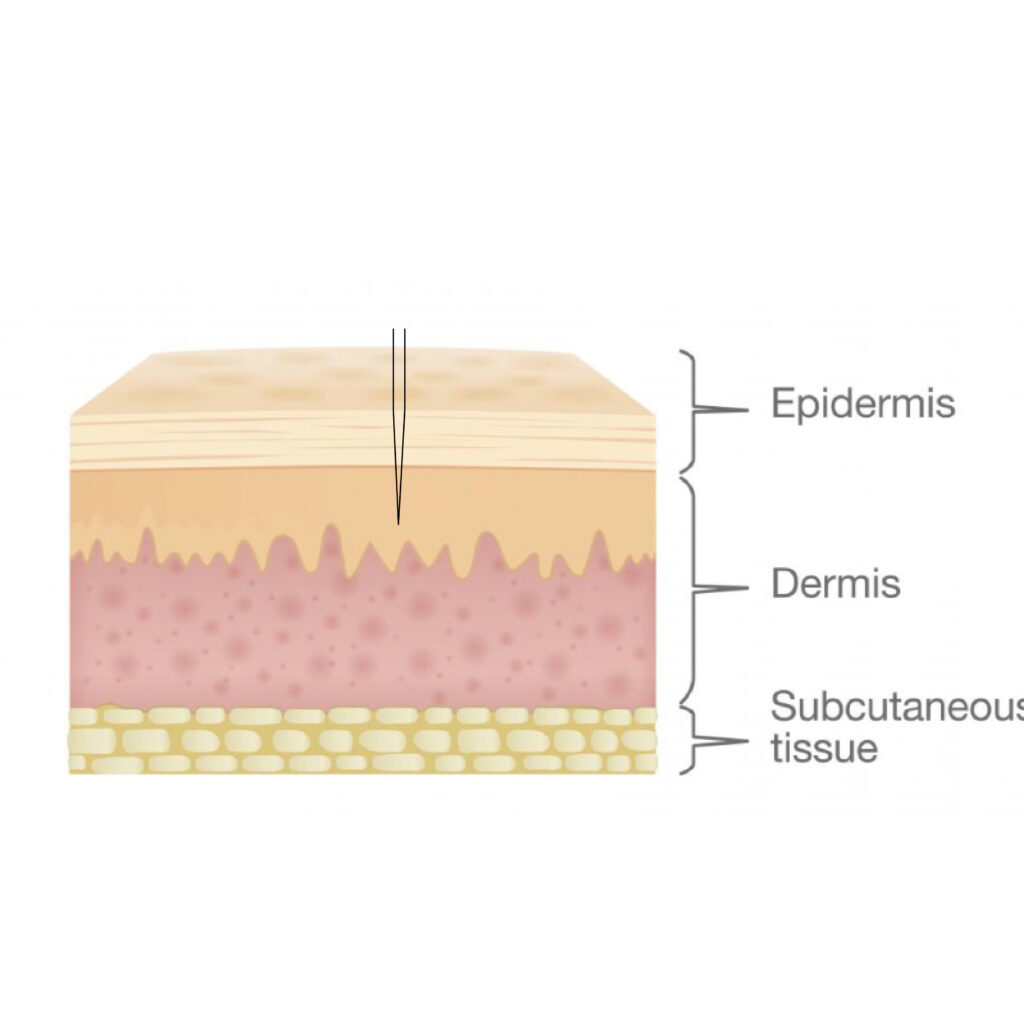
Thin Skin Normal Oily
On the temporal lobe, the skin is thinner. This leads to a deep application of pigment on the tails of the eyebrows, which in turn complicates the removal with a laser.
Tails of Eyebrows Forehead
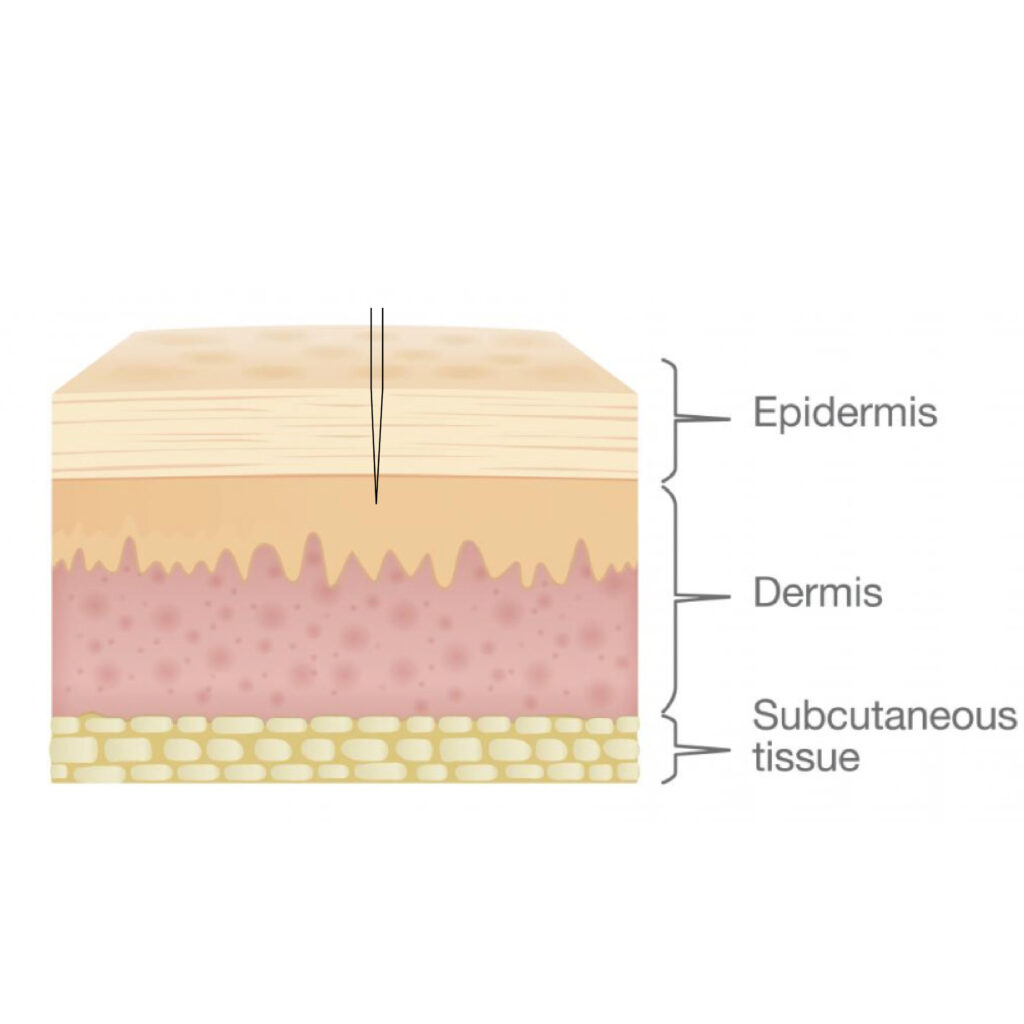
To get a good residue and predictable color, it is necessary to work in the upper layer of the dermis.
Another problem of the pigment residue is associated with oily skin since the oily skin has a thick layer of the epidermis and the pigment simply does not reach the dermis. In this case, the artists mistakenly make the decision to make more passes, instead of increasing the pressure on the skin.
- Oily Skin
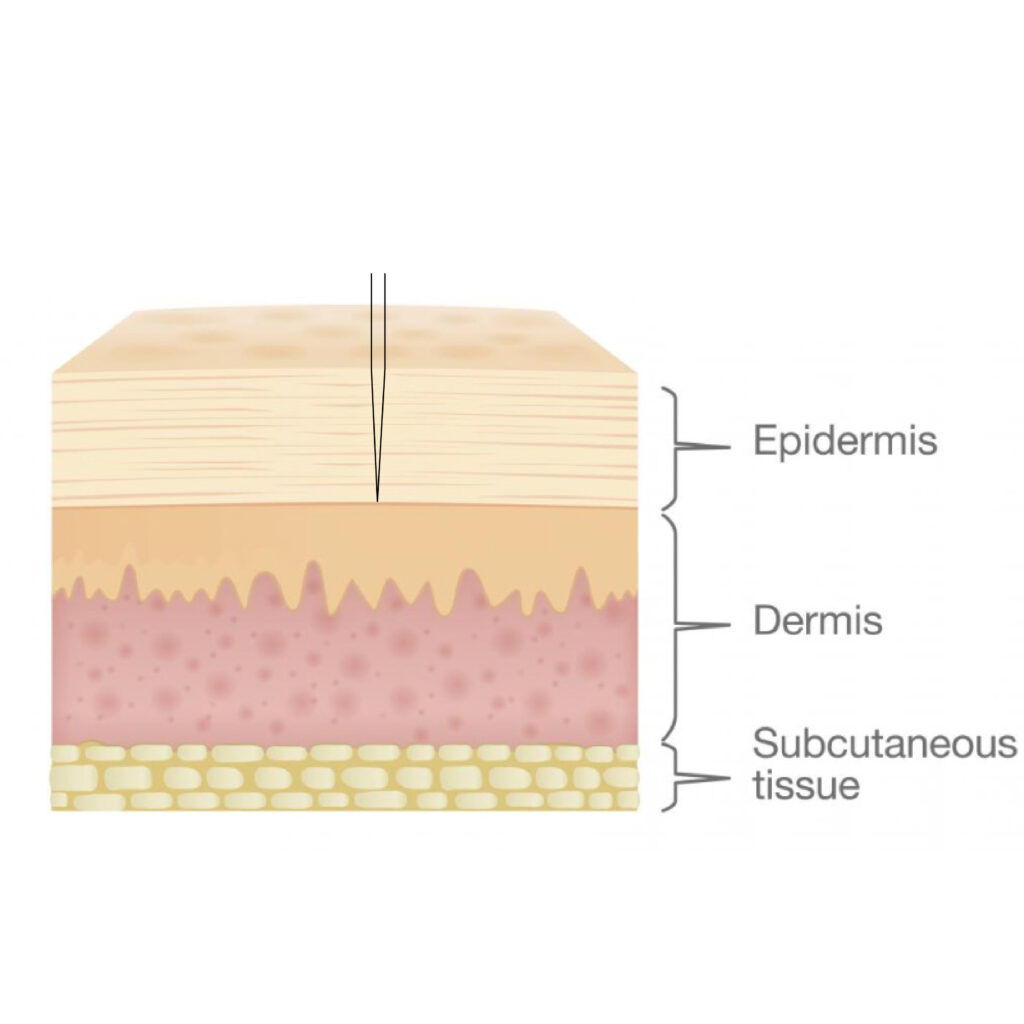
Let’s talk a little about color perception. Why sometimes we see blue eyebrows at clients.
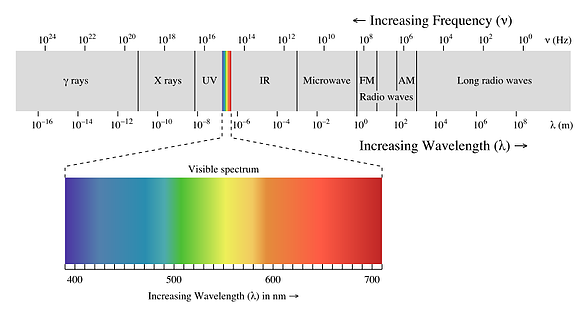
We perceive only a small spectrum of waves. That is if the retina of the eye (in our view) is the wavelength for example from 500-550 nanometers our brain tells us that it is green. If the wavelength is around 700 nm then the brain tells us it is red, etc. Different people perceive colors differently, there are for example colorists who perceive a very large range of colors, and there are men)))) Pale-red, dark-red for them all of this simply red) I’m just kidding) Another point that speaks of the difference in color perception is colorblind people. Everyone sees red as red, but they do not see it.
Another point, why do we see objects of different colors?
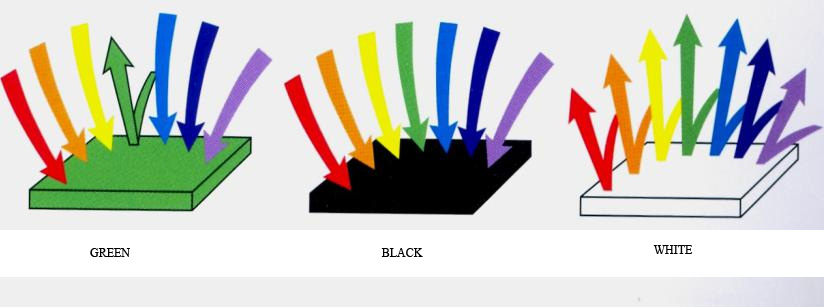
Sunlight consists of all wavelengths. We see white objects when the surface fully reflects the entire spectrum of waves, black when the surface absorbs the entire spectrum and does not reflect anything. If we see green blue or any other color, this means that all wavelengths are absorbed and the green or blue spectrum is reflected.
Black color absorbs any wavelengths, and white reflects them as much as possible, so white objects heat up less than black in the sun as everybody knows.
This is directly related to us because the laser is also a light of a certain wavelength.
The black color will be removed by a wave of any length, as it absorbs everything. If there is a white pigment, it is very hard to removed as it reflects them.
Ok, Let’s go to the next lesson
